Page 210 - Tata_Chemicals_yearly-reports-2020-2021
P. 210
Integrated Annual Report 2020-21
Market risk
Market risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market
prices. Market risk comprises three types of risk: currency risk, interest rate risk and other price risk, such as equity price risk and
commodity risk. The value of a financial instrument may change as a result of changes in the interest rates, foreign currency exchange
rates, equity price fluctuations, liquidity and other market changes. Financial instruments affected by market risk include loans and
borrowings, deposits, investments and derivative financial instruments.
Foreign currency risk management
Foreign exchange risk arises on future commercial transactions and on all recognised monetary assets and liabilities, which are
denominated in a currency other than the functional currency of the Company. The Company’s management has set a policy
wherein exposure is identified, a benchmark is set and monitored closely, and accordingly suitable hedges are undertaken. The
policy also includes mandatory initial hedging requirements for exposure above a threshold.
The Company's foreign currency exposure arises mainly from foreign exchange imports, exports and foreign currency borrowings,
primarily with respect to USD.
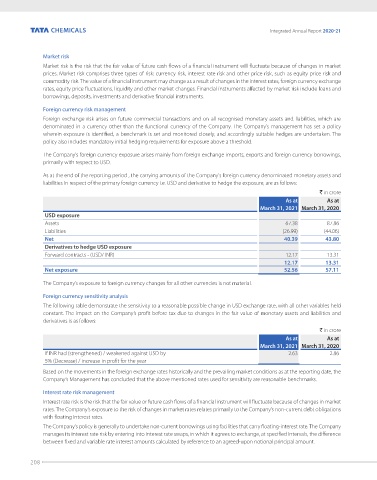
As at the end of the reporting period , the carrying amounts of the Company's foreign currency denominated monetary assets and
liabilities in respect of the primary foreign currency i.e. USD and derivative to hedge the exposure, are as follows:
` in crore
As at As at
March 31, 2021 March 31, 2020
USD exposure
Assets 67.38 87.86
Liabilities (26.99) (44.06)
Net 40.39 43.80
Derivatives to hedge USD exposure
Forward contracts - (USD/ INR) 12.17 13.31
12.17 13.31
Net exposure 52.56 57.11
The Company’s exposure to foreign currency changes for all other currencies is not material.
Foreign currency sensitivity analysis
The following table demonstrate the sensitivity to a reasonable possible change in USD exchange rate, with all other variables held
constant. The impact on the Company’s profit before tax due to changes in the fair value of monetary assets and liabilities and
derivatives is as follows:
` in crore
As at As at
March 31, 2021 March 31, 2020
If INR had (strengthened) / weakened against USD by 2.63 2.86
5% (Decrease) / increase in profit for the year
Based on the movements in the foreign exchange rates historically and the prevailing market conditions as at the reporting date, the
Company’s Management has concluded that the above mentioned rates used for sensitivity are reasonable benchmarks.
Interest rate risk management
Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market
rates. The Company’s exposure to the risk of changes in market rates relates primarily to the Company’s non-current debt obligations
with floating interest rates.
The Company’s policy is generally to undertake non-current borrowings using facilities that carry floating-interest rate. The Company
manages its interest rate risk by entering into interest rate swaps, in which it agrees to exchange, at specified intervals, the difference
between fixed and variable rate interest amounts calculated by reference to an agreed-upon notional principal amount.
208